Integrated aquaculture is defined as aquaculture that makes better use of resources. It reduces the potential excess of material or resources, including the excess organic material generated in primary fish farming, by introducing secondary farmed species. The results are a positive impact on the environment, the diversification of species and economic benefits.
In aquaculture, one of the most recommended ways to minimise the environmental impact and take better advantage of resources is multi-trophic farming.
The term multi-trophic refers to species’ use of different levels of the trophic chain, and this is the main point of differentiation with aquatic polyculture, in which diverse fish species are cultured at the same trophic level. Integrated multi-trophic aquaculture borrows a concept from nature, because in the food chain, some species find their food niche in the waste generated by others.
Multi-trophic systems in aquaculture, or integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, is a practice in which several aquaculture systems interact with one another, and the waste generated by some species is used as food or fertilizer by others. This creates a sustainable system that aims to reduce or eliminate the negative effects of animal farming in the area, improving environmental sustainability, economic stability (through product diversification) and social acceptability.
Ideally, the biological and chemical processes in a multi-trophic system are balanced. This balance is achieved through the appropriate selection of the different species used. Cultivated species must be more than just biofilters, because for the project to have viability and continuity, they must also add commercial value.
The basic model that exemplifies this type of system would consist of the combined farming of fish, bivalve molluscs and macroalgae.
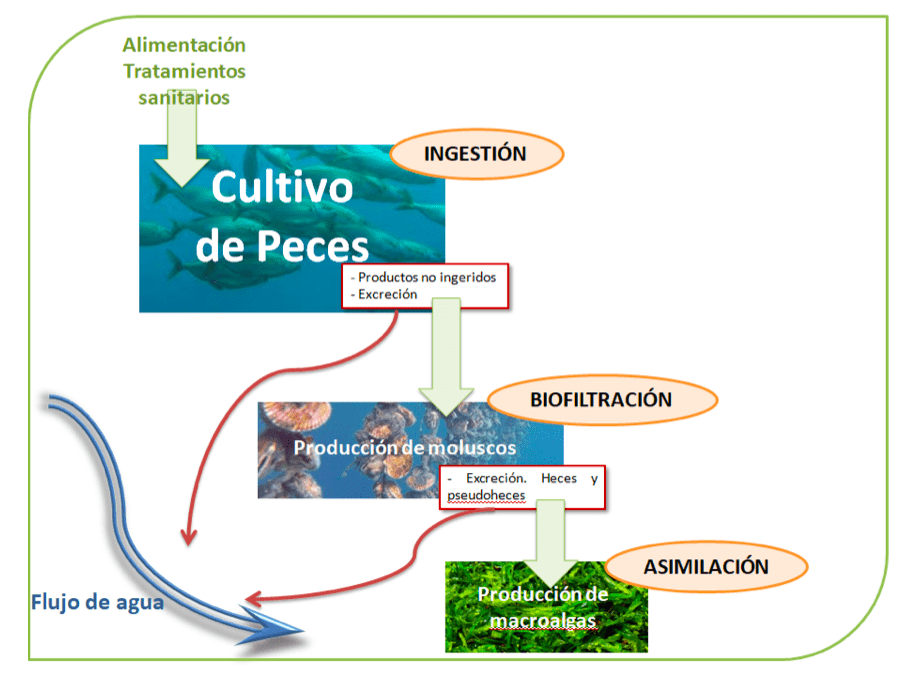
In real examples, it has been possible to verify how the particles discarded in marine cages, including food from the feed provided, are used by mussels and other bivalves. At the same time, the algae absorb inorganic waste generated by the farm. This ‘natural recycling system’ of aquaculture nutrients leads to a reduction of waste in the environment.
In short, it is an emerging activity with excellent prospects for the future, although it faces major challenges, such as:
- Lack of familiarity with some of the cultivated species.
- Suitable management of cultivations, as producers are usually highly specialised in monoculture.
- Identifying the appropriate species for each market.
- Economic viability.
Lastly, it is important to add that the FAO has emphasised on numerous occasions that the ‘development of integrated multi-trophic production systems’, among other advances in aquaculture research, helps to ‘mitigate the environmental impact (of marine farms)’. The United Nations organisation has thus recognised the efficiency of multi-trophic systems in this regard.
Sources: AQUAHOY ACUICULTURAMARINA MAPA FAO.

